|

|

|

|

|

|
Synthetic Methodologies
The application of new synthetic methodologies to structurally complex compounds having diverse functionalities, such as glycomimetics, is expected to significantly improve the understanding of reaction transformations and to favour the discovery of new reactions. In return, modern reactions are powerful tools for glycochemistry and glycobiology and are expected to accelerate the synthesis, and thus the discovery, of glycomimetics of biological interest.
Selected examples:
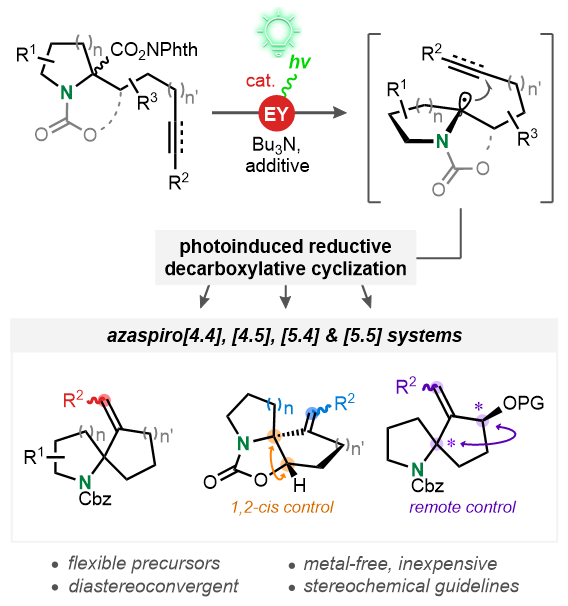
Towards a General Access to 1-Azaspirocyclic Systems via Photoinduced, Reductive Decarboxylative Radical Cyclization
Chem. Eur. J. 2024, e202303841-Hot paper.
Simple and versatile. A strategy for the construction of important 1-azaspirocyclic scaffolds is described. Alkynyl-tethered N-hydroxyphthalimide esters, swiftly assembled through an alkylation/deprotection/activation sequence, undergo photoinduced reductive decarboxylative radical 5-exo and 6-exo-dig cyclizations employing eosin Y (EY) as inexpensive photocatalyst. The key step can proceed in a diastereoconvergent manner and affords diverse ring systems relevant to medicinal chemistry and natural products.
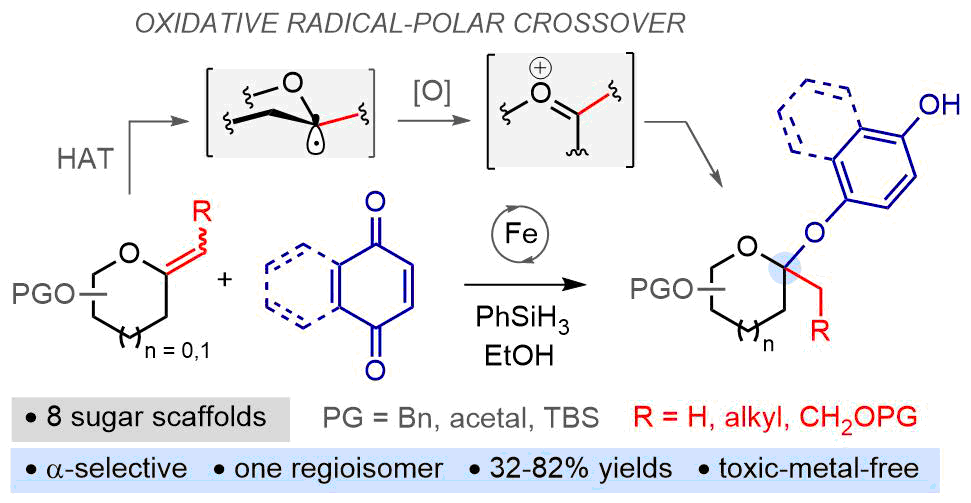
Formal Glycosylation of Quinones with exo-Glycals Enabled by Iron-mediated Oxidative Radical-polar Crossover
J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 13178-13194.
Formal glycosylation of quinones! The intermolecular C-O coupling reaction of 1,4-quinones with exo-glycals under iron-hydride hydrogen-atom transfer (HAT) conditions is described. This method provides a direct and regioselective access to a wide range of phenolic O-ketosides related to biologically relevant natural products in diastereomeric ratios up to > 98:2. The results of mechanistic experiments suggest that the key C-O bond-forming event proceeds through an original oxidative radical-polar crossover process involving a single-electron transfer between the HAT-generated glycosyl radical and the electron-acceptor quinone.
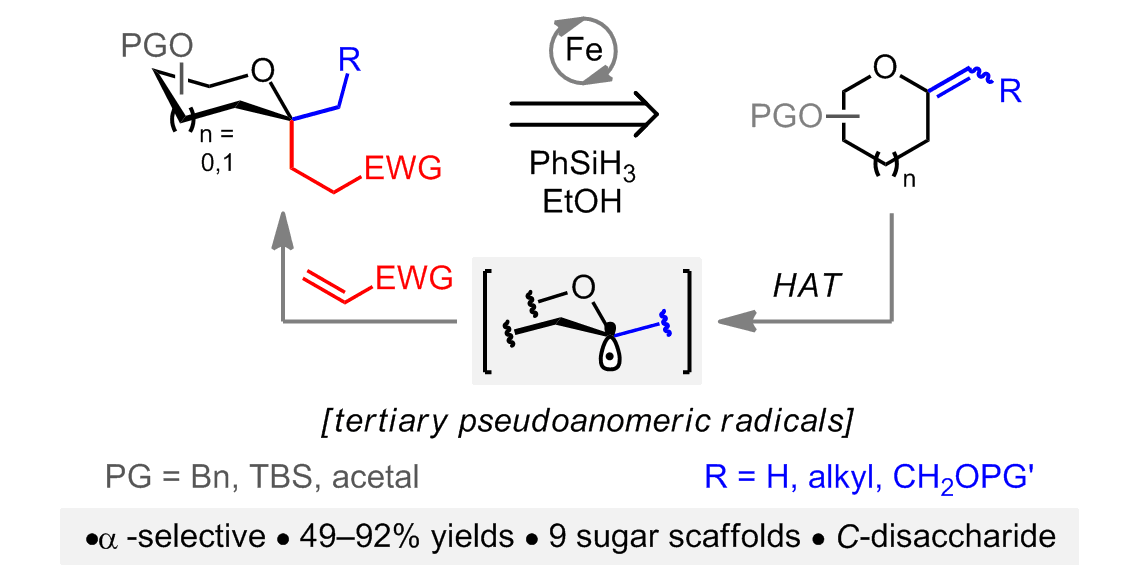
Stereoselective Synthesis of C,C-Glycosides from Exo-Glycals Enabled by Iron-Mediated Hydrogen Atom Transfer
Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 7262-7267.
C,C-Glycosides! C-glycosides as stable analogs of native sugars stand as one of the most important classes of carbohydrate mimetics. Significant challenges arise when considering the preparation of C,C-glycosyl compounds. These derivatives embed a stereodefined quaternary pseudoanomeric carbon which is difficult to construct using common methods. Readily available exo-glycals undergo hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) under iron-catalyzed conditions opening a path to mostly elusive tertiary pseudoanomeric radicals. Interception of the latter by electron-deficient olefins enable a novel, highly stereoselective synthesis of C,C-glycosides that precludes prior access to typically unstable and toxic glycosyl bromides or -selenides. The present method should offer a valuable tool for the synthesis of quaternary carbon-containing tetrahydropyran and tetrahydrofuran motifs which can be found in numerous synthetic drugs and natural products including maitotoxin.
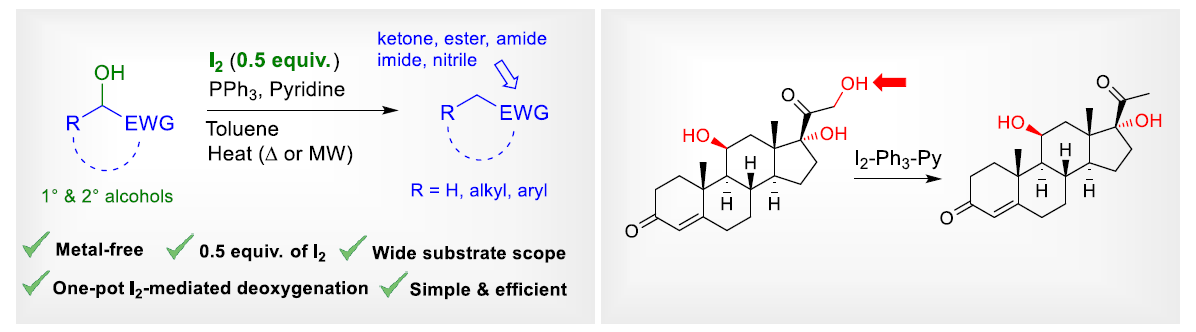
Metal-Free Iodine-mediated Deoxygenation of Alcohols in α-Position to Electron-withdrawing Group
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 1538-1545.
Surgical deoxygenation. The use of sub-stoichiometric amount of molecular iodine in the presence of Ph3P and pyridine effects a direct deoxygenation of primary and secondary alcohols in α-position to a variety of activating electron-withdrawing groups including ketones, esters, amides, imides and nitrile groups.